Sys_auto_sql_tuning_task 12c
- Oracle Sys_auto_sql_tuning_task
- Sys_auto_sql_tuning_task 12c Calculator
- Sys_auto_sql_tuning_task 12c Download
- Sys_auto_sql_tuning_task 12c Battery
The SETAUTOTUNINGTASKPARAMETER procedures are overloads that accept both string and numeric parameter values. These replace DBMSSQLTUNE.SETTUNINGTASKPARAMETER as the preferred way to amend the parameters for the SYSAUTOSQLTUNINGTASK task. The parameters that can be amended are listed here. Sysautosqltuningtask completed 03-jul-16 06:00 SYSAUTOSQLTUNINGTASK COMPLETED 04-JUL-16 22:01 You will get the last execution date-time and status of Automatic SQL Tuning Task (SYSAUTOTUNINGTASK) or you will get the message No rows selected.
Oracle 12c offers a useful utility called the SQL Tuning Advisor. You can use this built-in tool to provide suggestions or recommendations about certain SQL statements. Although it may not always give perfect advice, just like anything else, having it in your toolbox of tuning techniques is beneficial.
Use PL/SQL and the internal package DBMS_SQL_TUNE to create a tuning task. Type this:
You should see the following:
In the preceding command, note the TIME_LIMIT of 60. That limits the processing time to 60 seconds. You may not always want to run something like this for long periods in your database, because it incurs system overhead.
Execute the tuning advisor with your task by typing this:
Because of the limit of 60 seconds provided in the task creation, this step may take up to 60 seconds to complete. During this time, your prompt won’t come back.
When it completes, you should see this:
If you’ve set a longer time and are getting impatient, you can open another SQL window to make sure that the task is still executing by typing
You see something like the following:
When the execution is complete, you can view the results by running the BMS_SQLTUNE.report_tuning_task procedure. Type the following:
For the sake of space, we’ve snipped some sections from the output that follows, but you see something like this:
The latter part of the report shows the before and after execution plans. In this case, you’ve seen the before when you were generating execution plans. Go ahead and add the index, regenerate the execution plan, and see whether you’ve made an improvement.
Before you add the index, note that the recommendations give the SQL to add the index:
Also note that Oracle gives a warning:
Add the index with your own name by typing this:
You should see something like the following:
Take a look at the execution plan. Type the following:
And then type
You should see output like this:
Now that you’ve added the index, a few things are evident:
The cost of the plan dropped from 40336 to 5.
There are now six steps.
The full table scan is gone. Instead you see the use of your new index.
Often one of the tough parts about tuning a database is having a solid understanding of the application and the data. The issue might not always be obvious. Sometimes engaging other application and data experts helps.
Explain to them your findings and what you propose. They may be able to help you come to a conclusion. Also, if the data is part of a packaged third-party application, sometimes opening a ticket with the vendor is the way to go.
The DBMS_AUTO_SQLTUNE package is the interface for managing the Automatic SQL Tuning task. Unlike DBMS_SQLTUNE, the DBMS_AUTO_SQLTUNE package requires the DBA role.
The chapter contains the following topics:
Overview
Security Model
Using DBMS_AUTO_SQLTUNE
Overview
The DBMS_AUTO_SQLTUNE package is the interface to SQL Tuning Advisor (DBMS_SQLTUNE) when run within the Autotask framework. The database creates the automated system task SYS_AUTO_SQL_TUNING_TASK as part of the catalog scripts. This task automatically chooses a set of high-load SQL from AWR and runs the SQL Tuning Advisor on this SQL. The automated task performs the same comprehensive analysis as any other SQL Tuning task.
The automated task tests any SQL profiles it finds by executing both the old and new query plans. Automatic SQL Tuning differs from manual SQL tuning in one important way. If automatic implementation of SQL profiles is enabled (the default is disabled), then the database implements any SQL profiles that promise a great performance benefit. The implementation occurs at tuning time so that the database can immediately benefit from the new plan. You can enable or disable automatic implementation by using the SET_AUTO_TUNING_TASK_PARAMETER API to set the ACCEPT_SQL_PROFILES parameter.
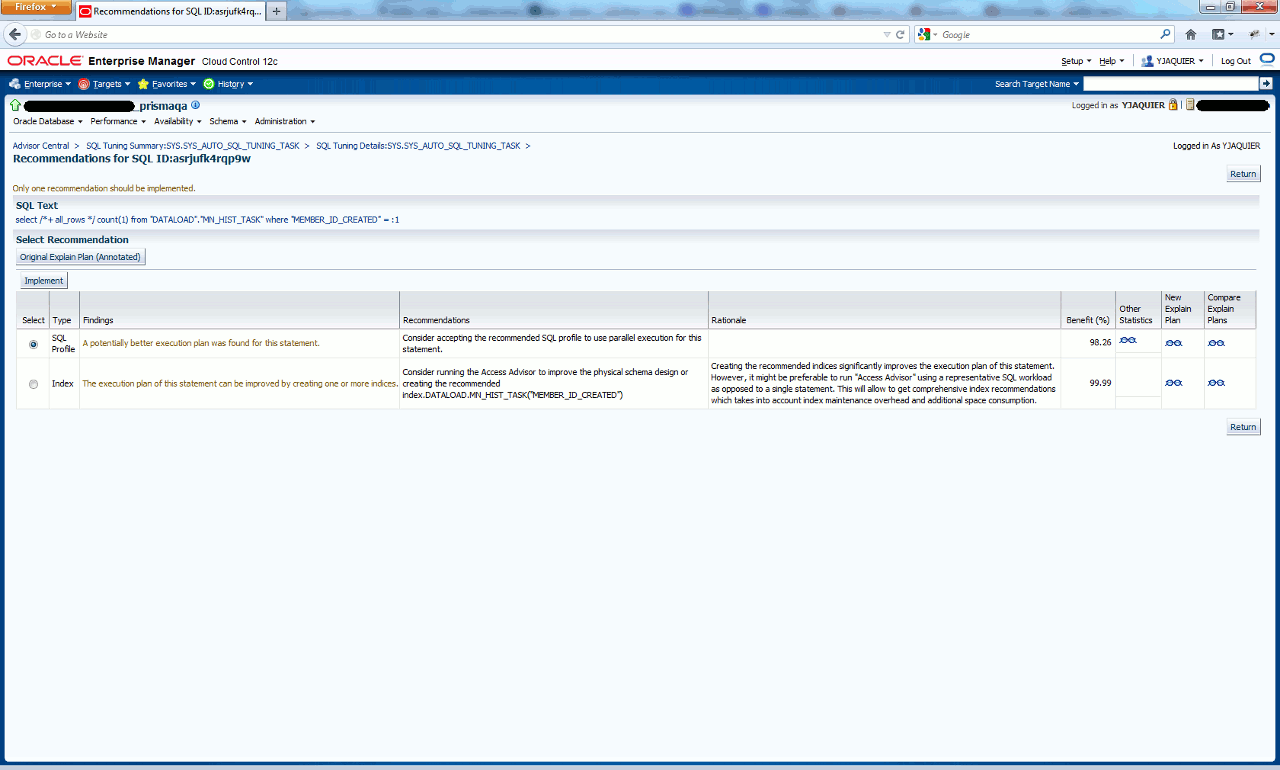
In each maintenance window, the automated tuning task stores its results as a new execution. Each execution result has the same task name but a different execution name. Query the DBA_ADVISOR_EXECUTIONS view for information about task executions. Use the REPORT_AUTO_TUNING_TASK Function to view reports that span multiple executions.
Security Model
This package is available to users with the DBA role. For other users, you must grant the EXECUTE privilege on the package explicitly. Note that the EXECUTE_AUTO_TUNING_TASK procedure is an exception: only SYS can invoke it.
Users can call APIs in this package to control how the automatic tuning task behaves when it runs, such as enabling automatic SQL profile creation and configuring the total and per-SQL time limits under which the task runs. Because these settings affect the overall performance of the database, it may not be appropriate for all users with the ADVISOR privilege to have access to this package.
Summary of DBMS_AUTO_SQLTUNE Subprograms
Table 30-1 DBMS_AUTO_SQLTUNE Package Subprograms
| Subprogram | Description |
|---|---|
Executes the Automatic SQL Tuning task immediately ( | |
Displays a text report of the automatic tuning task's history | |
Changes a task parameter value for the daily automatic runs |
EXECUTE_AUTO_TUNING_TASK Function & Procedure
This function and procedure executes the Automatic SQL Tuning task (SYS_AUTO_SQL_TUNING_TASK). Both the function and the procedure run in the context of a new task execution. The difference is that the function returns that new execution name. Note that only SYS can invoke this subprogram.
Oracle Sys_auto_sql_tuning_task
Parameters
Table 30-2 EXECUTE_TUNING_TASK Function & Procedure Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| A name to qualify and identify an execution. If not specified, it is generated by the advisor and returned by function. |
| List of parameters (name, value) for the specified execution. The execution parameters have effect only on the execution for which they are specified. They override the values for the parameters stored in the task (set through the SET_AUTO_TUNING_TASK_PARAMETER Procedures). |
| A 256-length string describing the execution |
Sys_auto_sql_tuning_task 12c Calculator
Usage Notes
A tuning task can be executed multiple times without having to reset it.
REPORT_AUTO_TUNING_TASK Function
This procedure displays the results of an Automatic SQL Tuning task.
Parameters
Table 30-3 REPORT_TUNING_TASK Function Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Name of the beginning task execution to use. If |
| Name of the ending task execution to use. If |
| Type of the report to produce. Possible values are |
| Level of detail in the report:
|
| Section of the report to include:
|
| Advisor framework object id that represents a single statement to restrict reporting to. |
| Maximum number of SQL statements to show in the report |
Return Values
A CLOB containing the desired report.
SET_AUTO_TUNING_TASK_PARAMETER Procedures
This procedure updates the value of a SQL tuning parameter of type VARCHAR2 or NUMBER as used for the reserved auto tuning task, SYS_AUTO_SQL_TUNING_TASK.
Parameters
Table 30-4 SET_AUTO_TUNING_TASK_PARAMETER Procedure Parameters
Sys_auto_sql_tuning_task 12c Download
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Name of the parameter to set. The possible tuning parameters that can be set by this procedure using the parameter in the form
Audio vst free download. The following parameters are supported for the automatic tuning task only:
|
| New value of the specified parameter |